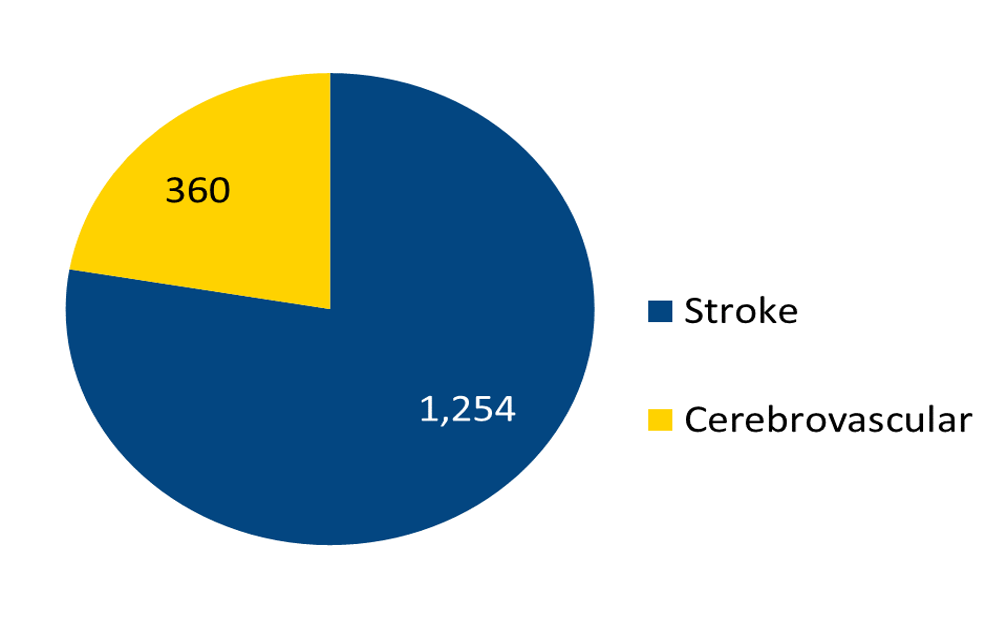
The Number of Patients Admitted with Stroke in 2023
For an explanation of the types of stroke, click here. The Cerebrovascular category is the number of patients who were admitted specifically for treatment of aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVM), and blockages of blood vessels (stenosis, occlusion). For more cerebrovascular information, click here. For more information about these problems and treatments at Barnes-Jewish Hospital, click here.
Definitions:
Ischemic Stroke: Stroke caused by an obstruction within a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain. Read more →
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Blood leakage inside the brain caused when a diseased blood vessel within the brain weakens or leaks.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding outside the brain, usually from the rupture of a brain aneurysm.
TIA: Abbreviation for transient ischemic attack. A temporary episode of stroke symptoms, which go away completely in less than 24 hours. Caused by temporary decreased blood flow to part of the brain. Read more →
Definitions:
Aneurysm: A weak spot in a blood vessel, which may burst, causing a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Read more →
AVM: Arteriovenous malformation, a collection of abnormal veins and arteries, which may bleed, causing intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Read more →
Moyamoya: Progressive narrowing of the larger vessels at the base of the brain. Can lead to ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage. Read more →
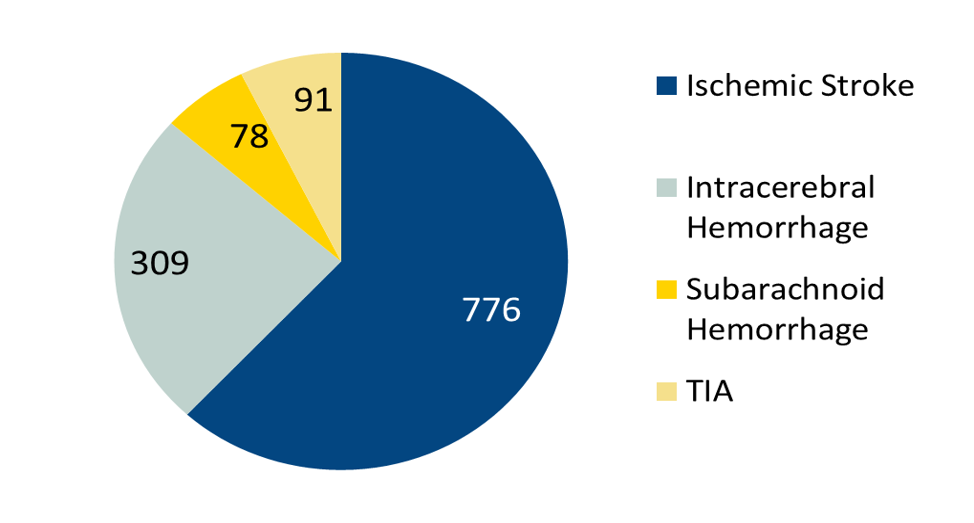
Types of Stroke
For an explanation of the types of stroke, click here.
| Types of Stroke |
# Cases |
| Ischemic Stroke |
776 |
| Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
309 |
| Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
78 |
| TIA |
91 |
| Total: |
1,254 |
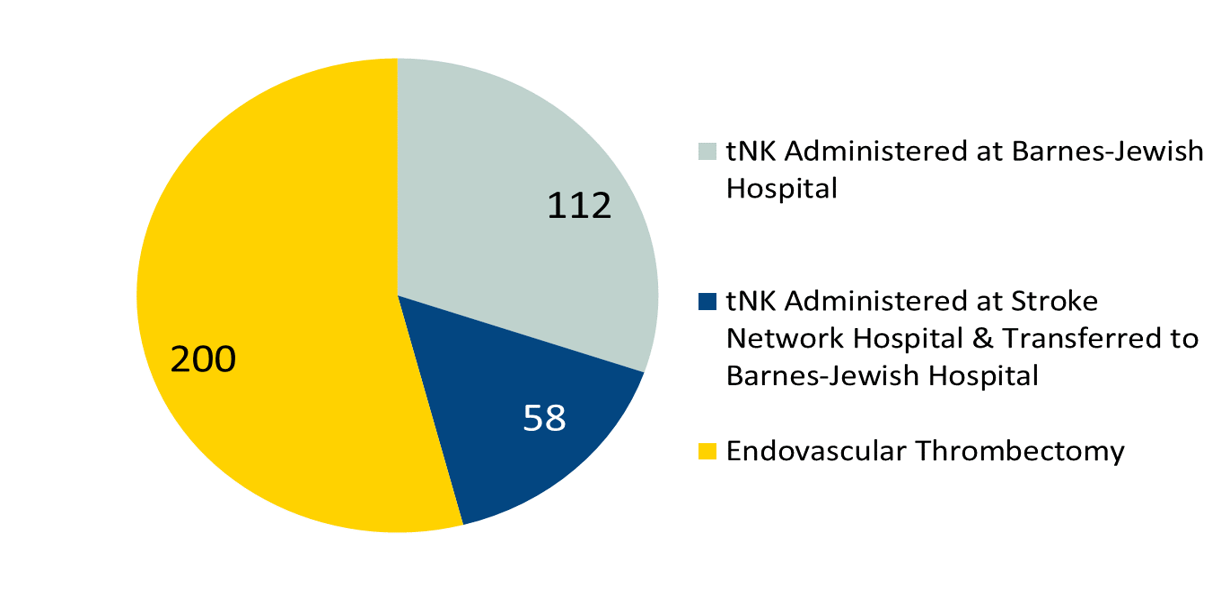
Ischemic Stroke Treatment
The number of patients treated at Barnes-Jewish Hospital who received tPA for their ischemic stroke, and those who were considered for endovascular thrombectomy therapy. For more information on these treatments, click here.
Definitions:
tPA Administered in BJH ED: tPA is a clot-busting drug used to dissolve the blockage in a blood vessel that is causing an ischemic stroke, to restore blood flow, and help prevent disability after a stroke.
Definitions:
Endovascular Thrombectomy: Minimally invasive (catheter-based) angiography procedure to treat stroke by mechanically retrieving a blood clot.
Endovascular Thrombectomy Therapy: a procedure where a blockage in a blood vessel is removed by a catheter inserted into the blocked artery.
Ischemic Stroke Treatment Outcomes
Ischemic stroke patients who develop a symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (i.e., clinical deterioration ≥ 4 point increase on NIHSS and brain image finding of parenchymal hematoma, or subarachnoid hemorrhage, or intraventricular hemorrhage) within (≤) 36 hours after the onset of treatment with intra-venous (IV) or intra-arterial (IA) thrombolytic (t-NK) therapy, or mechanical endovascular reperfusion procedure (i.e., mechanical endovascular thrombectomy with a clot retrieval device).
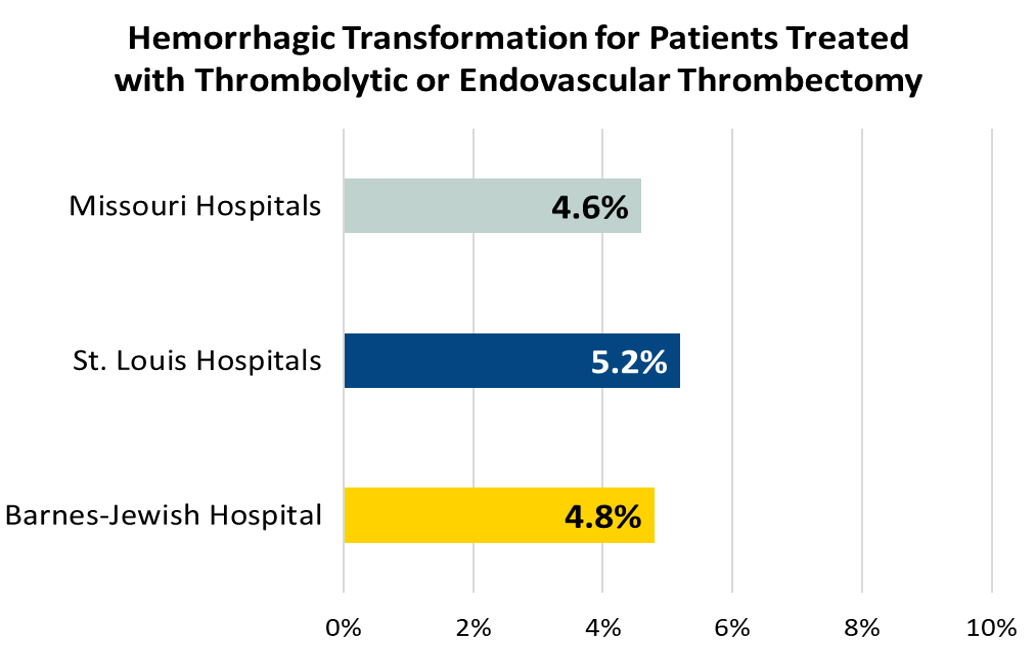
* Smaller numbers represent better outcomes.
Ischemic stroke patients with a post-treatment reperfusion grade of TICI 2B or higher in the vascular territory beyond the target arterial occlusion at the end of treatment with intra-arterial (IA) thrombolytic (t-NK) therapy and/or mechanical endovascular reperfusion therapy

*Many of our patients are able to go home 48 hours post thrombectomy. These patients are not included in the GWTG data.
**TICI score = Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction in Reperfusion Grade
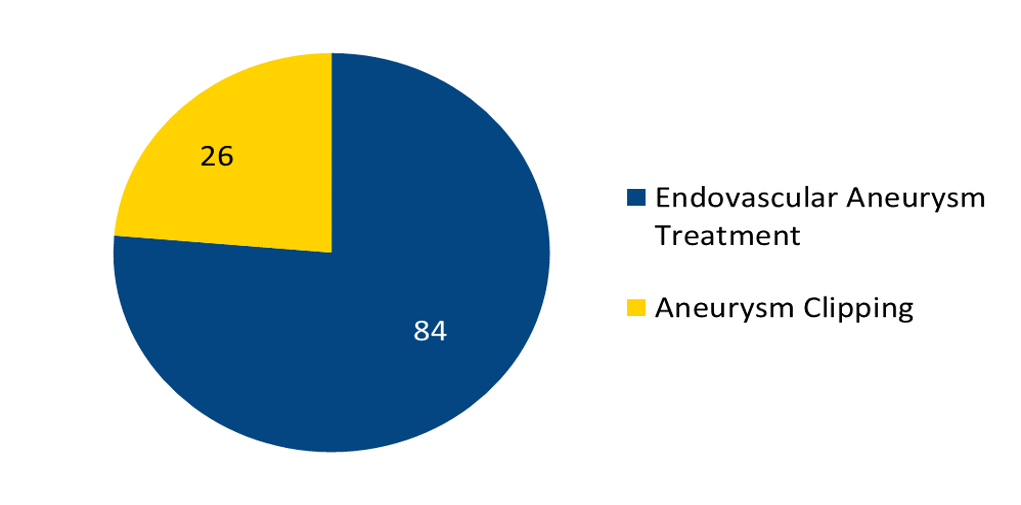
Aneurysm Treatment
For more information on Aneurysm clipping and coiling, click here.
Definitions:
Endovascular Coiling: A procedure where an angiogram is performed, and a catheter is used to place multiple small soft coils directly into the aneurysm to fill the space and prevent bleeding.
Definitions:
Aneurysm Clipping: Surgical procedure in which a clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to prevent it from rupturing.
From 2002 through 2020, more than 2,000 endovascular (coiling) procedures were performed at Barnes-Jewish Hospital to treat unruptured brain aneurysms. Of those cases, 67 had complications of stroke - a complication rate of 3.97%. Read more →
Joint Commission Performance Measures
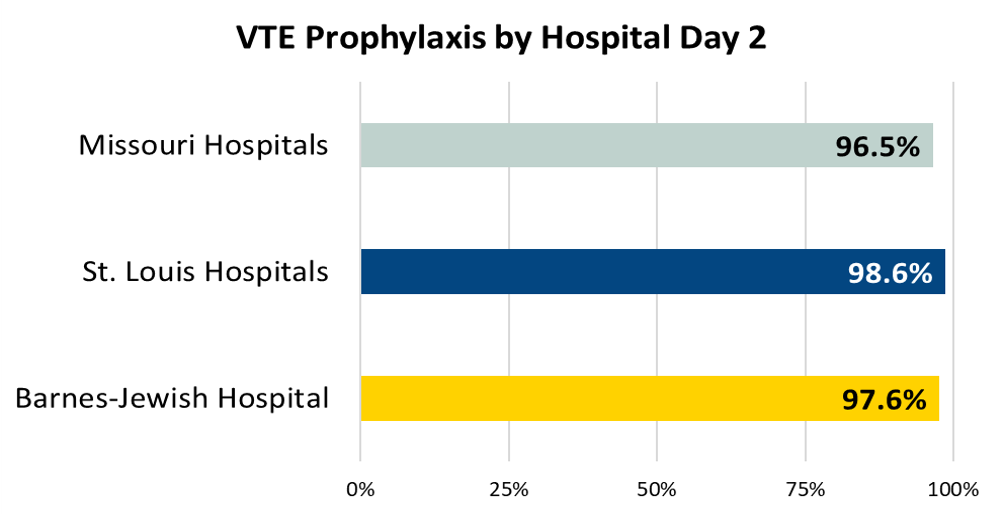
Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients who received VTE prophylaxis or have documentation why no VTE prophylaxis was given the day of or the day after hospital admission
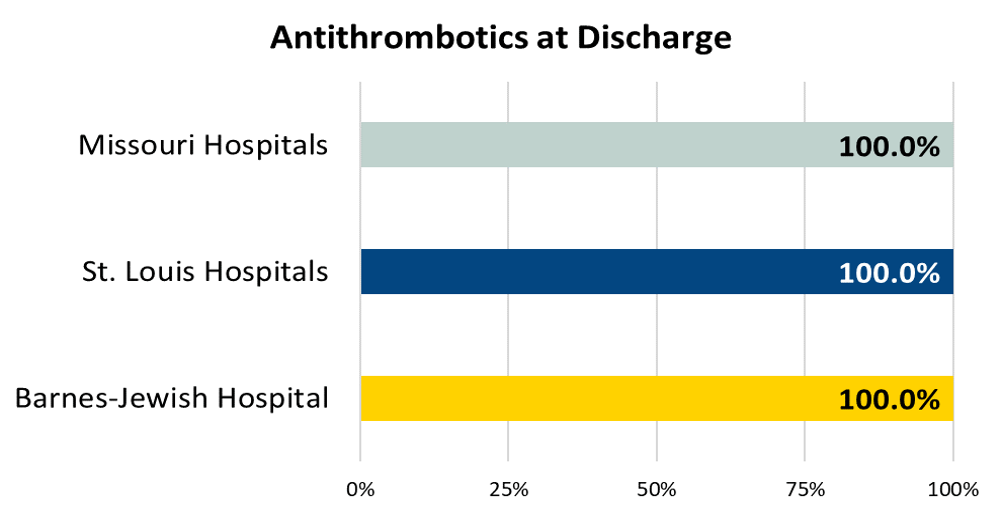
Ischemic stroke patients prescribed antithrombotic therapy at hospital discharge
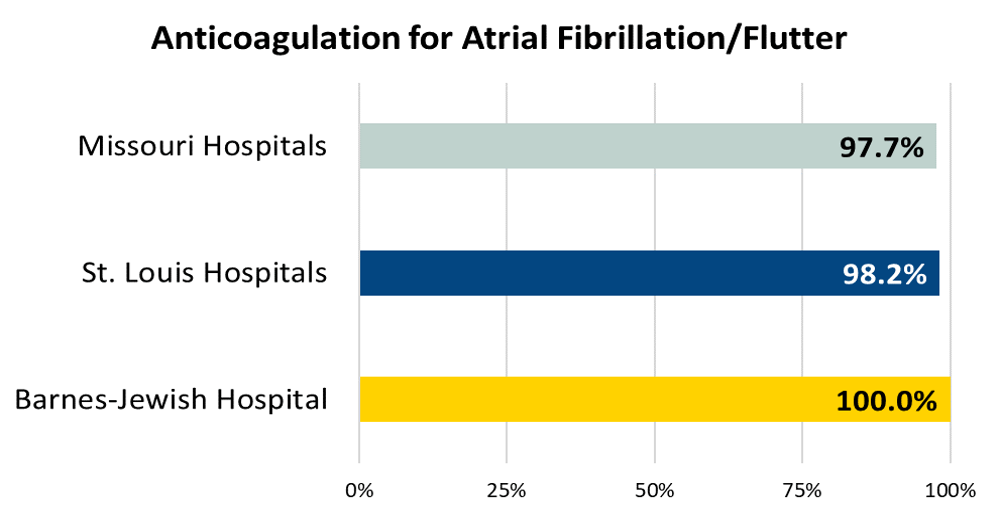
Ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter who are prescribed anticoagulation therapy at hospital discharge
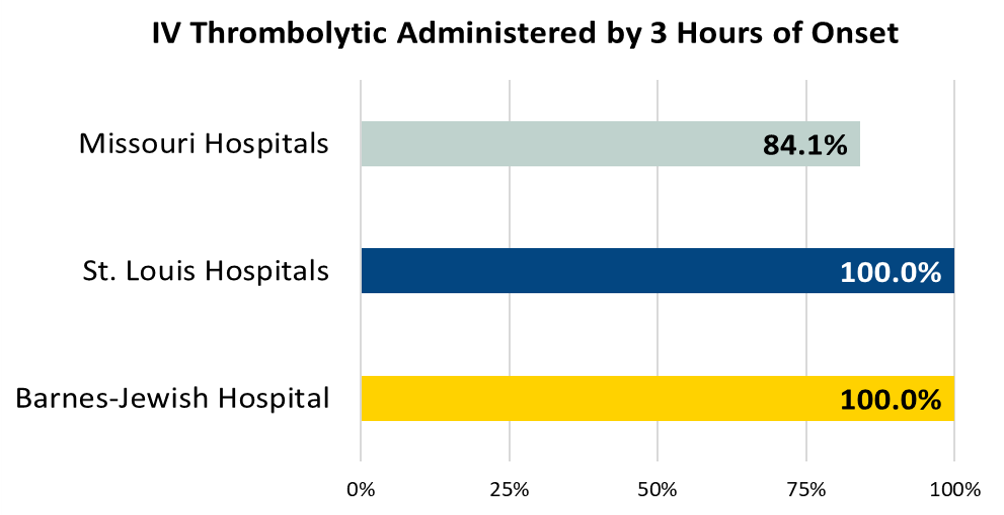
Acute ischemic stroke patients who arrive at this hospital within 2 hours of time last known well and for whom IV t-PA was initiated at this hospital within 3 hours of time last known well.
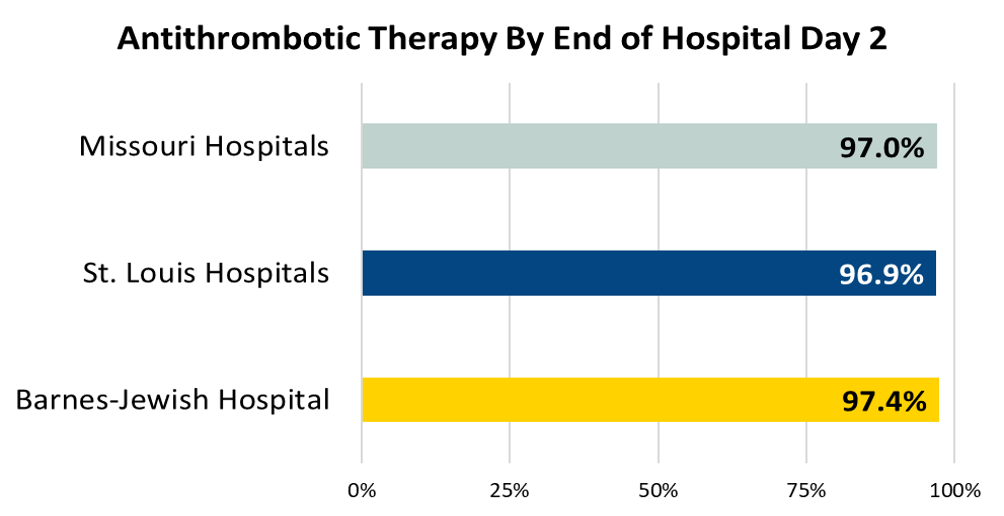
Antithrombotic Therapy By End of Hospital Day 2
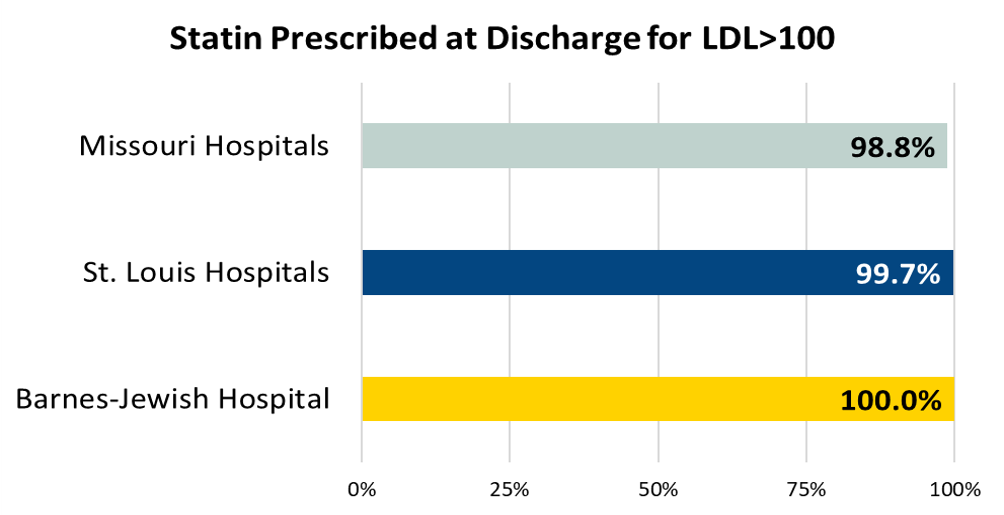
Ischemic stroke patients who are prescribed statin medication at hospital discharge
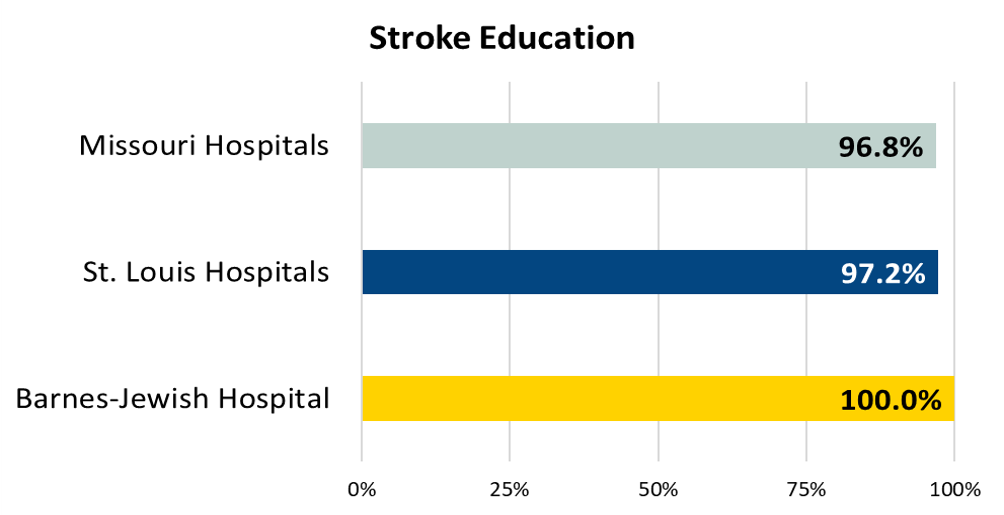
Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients or their caregivers who were given educational materials during the hospital stay addressing all of the following: activation of emergency medical system, need for follow-up after discharge, medications prescribed at discharge, risk factors for stroke, and warning signs and symptoms of stroke
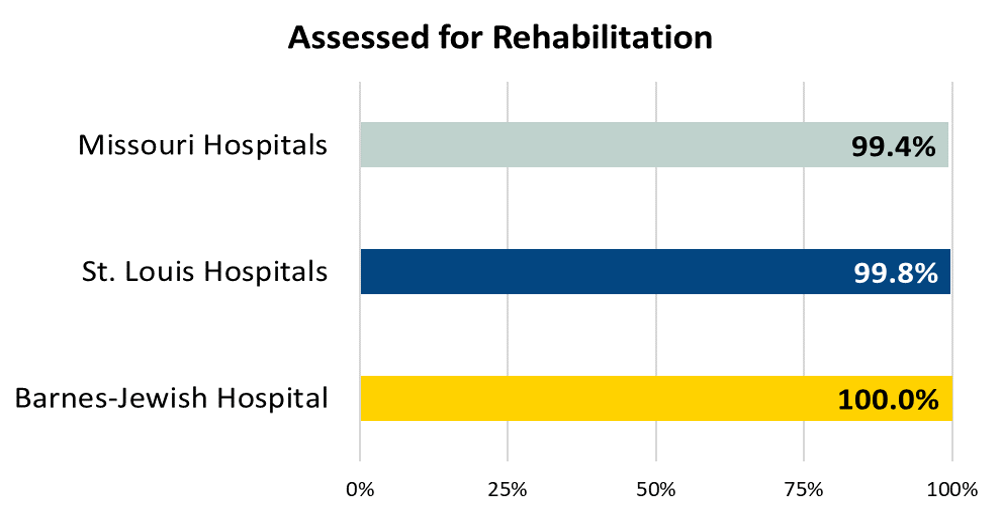
Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients who were assessed for rehabilitation services